2026 Top Battery Storage Trends to Watch Out For?
The battery storage industry is undergoing rapid transformation. With advancements in technology and growing demand for sustainable energy solutions, experts are keenly observing emerging trends. Dr. Emily Chen, a prominent figure in battery research, emphasizes, "The future of battery storage is not just about capacity; it’s about efficiency and integration."
In 2026, several key trends will shape the battery storage landscape. Innovations such as solid-state batteries promise increased safety and energy density. Meanwhile, smarter grid integration will enhance energy efficiency. This convergence of technology may redefine energy consumption patterns globally. Yet, challenges remain. Current recycling methods need improvement to address environmental concerns.
As we look ahead, it is essential to consider both opportunities and challenges. The potential for battery storage to revolutionize energy systems is immense. However, we must also navigate the hurdles of sustainability and infrastructure adaptation. Addressing these issues will be crucial for the industry’s future success.

Emerging Technologies in Battery Storage for 2026
The battery storage landscape is evolving rapidly. In 2026, several emerging technologies are set to reshape the industry. Solid-state batteries are gaining traction for their higher energy density. These batteries use solid electrolytes, improving safety and performance. The promise of longer life cycles can reduce long-term costs for users.
Another trend involves advanced lithium-sulfur batteries. This technology could offer significantly higher capacity compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. However, challenges remain. These include issues with stability and scalability. There is much work to be done to ensure reliability.
Additionally, look out for improved recycling processes. As battery demand grows, so does the need for sustainable solutions. New methods aim to recover more materials from used batteries. Progress in this area is vital, yet hurdles exist. Efficiency and effectiveness in recycling technologies still need refinement. Battery storage will not only transform energy use but also requires careful consideration of environmental impacts.
2026 Top Battery Storage Trends to Watch Out For
The chart above illustrates the projected market share for various battery storage technologies in 2026. Lithium-ion batteries are expected to maintain the largest share, while emerging technologies like solid-state and flow batteries are anticipated to grow significantly. Understanding these trends is crucial for adapting to the evolving energy landscape.
Sustainability Trends Influencing Battery Storage Development
The evolution of battery storage is significantly driven by sustainability trends. The urgency to combat climate change is reshaping energy systems worldwide. Renewable energy sources are becoming more prevalent. However, their intermittent nature poses challenges. This is where energy storage solutions step in. They enhance reliability and enable a smooth transition to cleaner power.
Emerging technologies aim to reduce the environmental impact of battery production. For instance, research focuses on sustainable materials like sodium and magnesium. These alternatives offer promising benefits to the ecosystem. Yet, challenges remain. Not all substitutes can match lithium's performance, leading to a complex decision-making process for developers.
Furthermore, recycling practices are gaining attention. Many batteries still end up in landfills, causing significant harm. Improved recycling methods can reclaim materials and lower demand for new resources. The journey towards sustainable battery storage is fraught with hurdles. These issues require more innovative solutions and collaboration among researchers, manufacturers, and policy-makers.
Innovations in Battery Materials and Their Impact
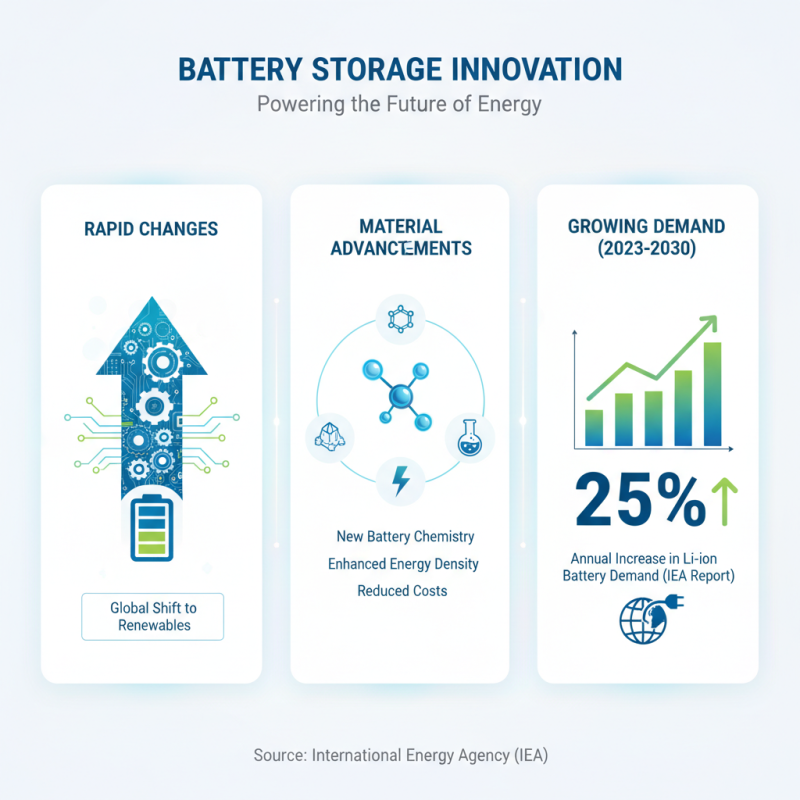
The battery storage sector is experiencing rapid changes. Innovations in battery materials play a crucial role. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency, the global demand for lithium-ion batteries is expected to increase by 25% annually through 2030. This surge will drive the need for advanced materials that can enhance energy density and reduce costs.
One notable trend is the development of solid-state batteries. These batteries promise higher energy efficiency and safety. However, challenges remain in scaling production for commercial use. Additionally, research indicates that replacing cobalt with alternative materials could reduce reliance on scarce resources. According to BloombergNEF, new material innovations could lower battery costs by nearly 15% in the next five years.
While these advancements are promising, they are not without limitations. Supply chain issues and environmental impacts from mining processes are significant concerns. Future innovations must address these negative consequences while enhancing performance. The path forward requires a balance between technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Market Drivers Shaping the Future of Energy Storage Solutions
As we approach 2026, the energy storage market is shifting rapidly. Renewable energy sources are driving demand for effective battery solutions. Improved technology offers higher capacity and efficiency, but many challenges remain. The integration of renewable energy into existing grids needs to be seamless. Local governments are pushing for sustainable practices, further fuelling innovation.
Market drivers include rising electricity prices and environmental regulations. Businesses seek ways to lower costs and reduce carbon footprints. However, there’s a risk of overestimating energy storage capabilities. As new technologies emerge, they must be rigorously tested. Reliable data is crucial for investors and developers alike.
Storage solutions must also address end-of-life concerns. Recycling and disposal remain significant hurdles. Additionally, public perception of battery technologies can be skeptical. Misconceptions linger about safety and environmental impact. Educational initiatives can bridge this gap, but they require time and effort. The future is promising, but real obstacles need tackling.
2026 Top Battery Storage Trends to Watch Out For
| Trend | Description | Impact Level | Expected Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-State Batteries | Transition from liquid to solid electrolytes for improved safety and energy density. | High | 60 |
| Recycling of Battery Materials | Increasing focus on sustainable practices to recover materials from used batteries. | Medium | 45 |
| Grid Storage Solutions | Battery systems designed specifically for energy storage in electricity grids. | High | 70 |
| Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) | Subscription-based models allowing users to leverage battery technology without ownership. | Medium | 50 |
| Advanced Management Systems | Integration of AI and IoT for optimized battery management and performance analytics. | High | 65 |
Regulatory Changes Affecting Battery Storage Adoption in 2026
In 2026, regulatory changes are set to transform the battery storage landscape. Governments worldwide are introducing new policies to support clean energy. These policies often aim to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy resilience. However, they can also create uncertainty for manufacturers and investors. Striking a balance between innovation and compliance remains a challenge.
Local incentives play a crucial role in adoption. States may offer tax credits or rebates for battery storage installations. Yet, inconsistent regulations can hinder progress. Some regions may lag, affecting overall growth. Companies must adapt quickly to shifting requirements, which can be exhausting.
Public awareness is growing, but misconceptions persist. Some people believe battery storage is still too expensive. While costs are declining, not everyone sees the benefits. Education efforts should focus on real-world applications and long-term savings. This gap in understanding may slow down adoption. As the regulatory landscape evolves, stakeholders must reflect on how to navigate these changes effectively.


